Jebel Hafit Tombs

Location and History
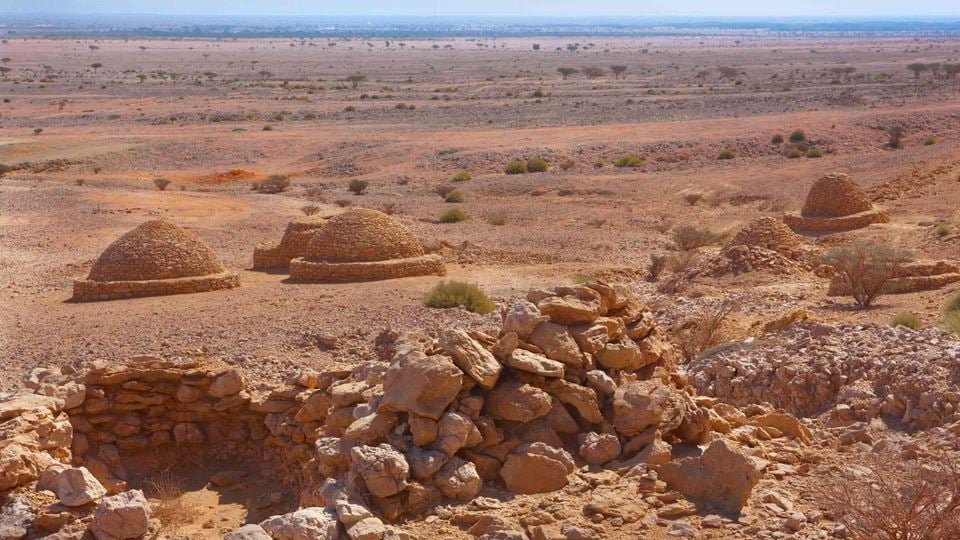
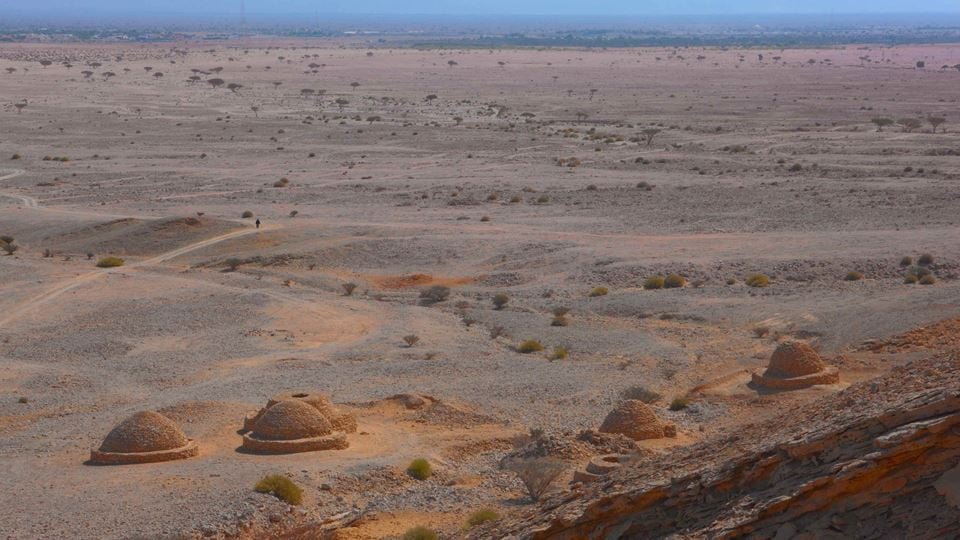
Location: The tombs are located on the foothills of Jebel Hafeet mountain in Al Ain city, within the Emirate of Abu Dhabi.
Dating: The tombs date back to the end of the 4th millennium BC, approximately 5,000 years ago, marking the beginning of the Bronze Age in the region.
Architectural Features
Number: Over 500 tombs have been discovered in the area.
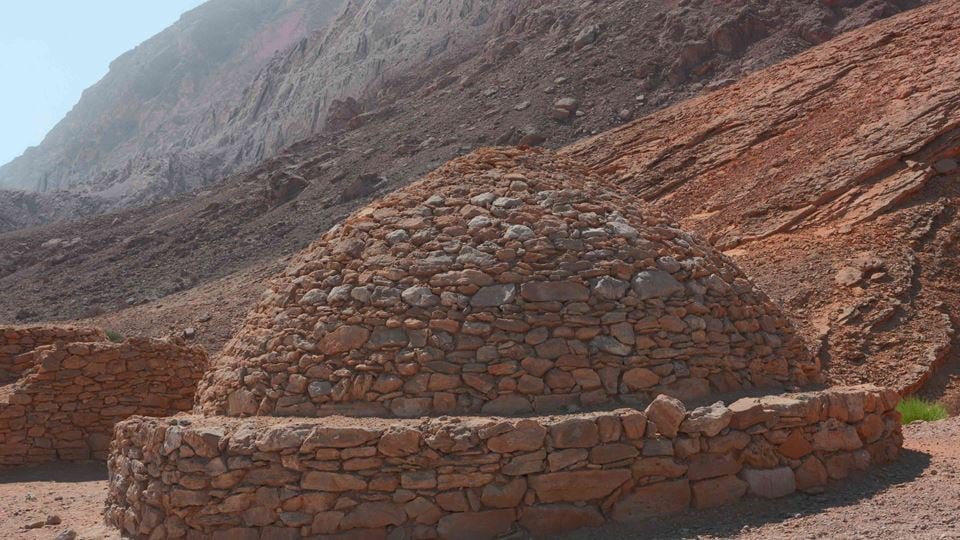
Shape: The tombs were constructed from local stones in a circular or oval shape.
Design: They are characterized by their “beehive” or “dome-like” structure, where the walls narrow towards the top to form a dome.
Burial Chamber: Each tomb contains a single burial chamber and a single entrance, often facing south.
Burials: These tombs were designated for the burial of two to five individuals at most, unlike the later “Umm Al Nar” tombs, which could accommodate a larger number of remains.


Archaeological Discoveries
Excavations conducted by archaeological missions, particularly the Danish expedition in 1959, uncovered numerous artifacts that highlight the site’s significance and its ancient trade connections:
Pottery: Small pottery vessels, imported from Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq), were found. These are known as “Jemdet Nasr” pottery, confirming the existence of ancient trade relations.
Copper Tools: Daggers and spearheads dating back to the 2nd millennium BC were discovered.
Jewelry: A collection of beads and other ornamental items was found.
Reuse: Some artifacts, such as vessels made from soft soapstone, indicate that the tombs were reused on multiple occasions, especially during the Iron Age (1000-600 BC).
Significance and Heritage
UNESCO List: The Jebel Hafeet tombs were added to the UNESCO World Heritage List as part of the cultural sites of Al Ain, highlighting their immense historical and human value.
Tourist Destination: The tombs are an ideal destination for visitors to explore the region’s ancient history, offering a unique experience amidst the natural landscape of Jebel Hafeet.